Kubernetes
Kubernetes
Kubernetes is a portable, extensible, open source platform for managing containerized workloads and services, that facilitates both declarative configuration and automation. It has a large, rapidly growing ecosystem. Kubernetes services, support, and tools are widely available.
Kubernetes Components
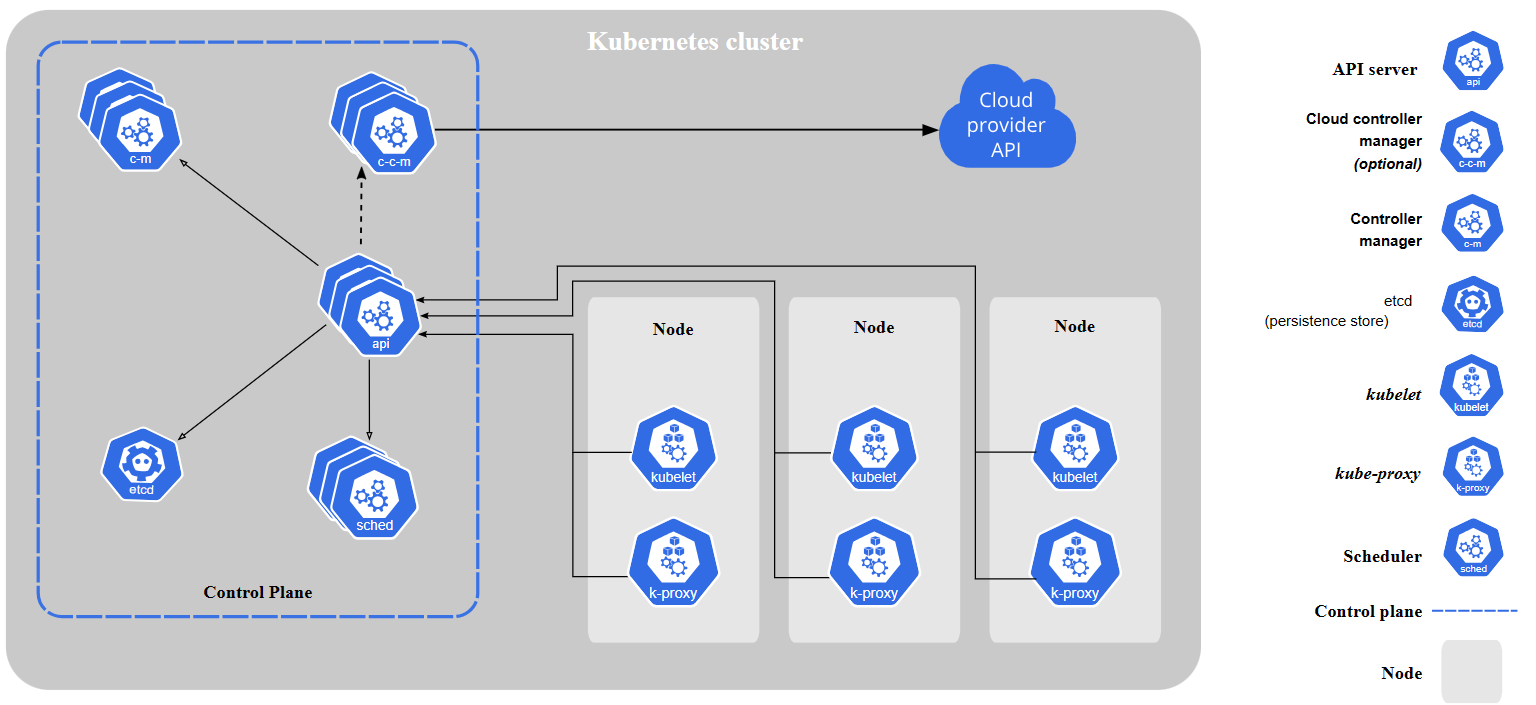
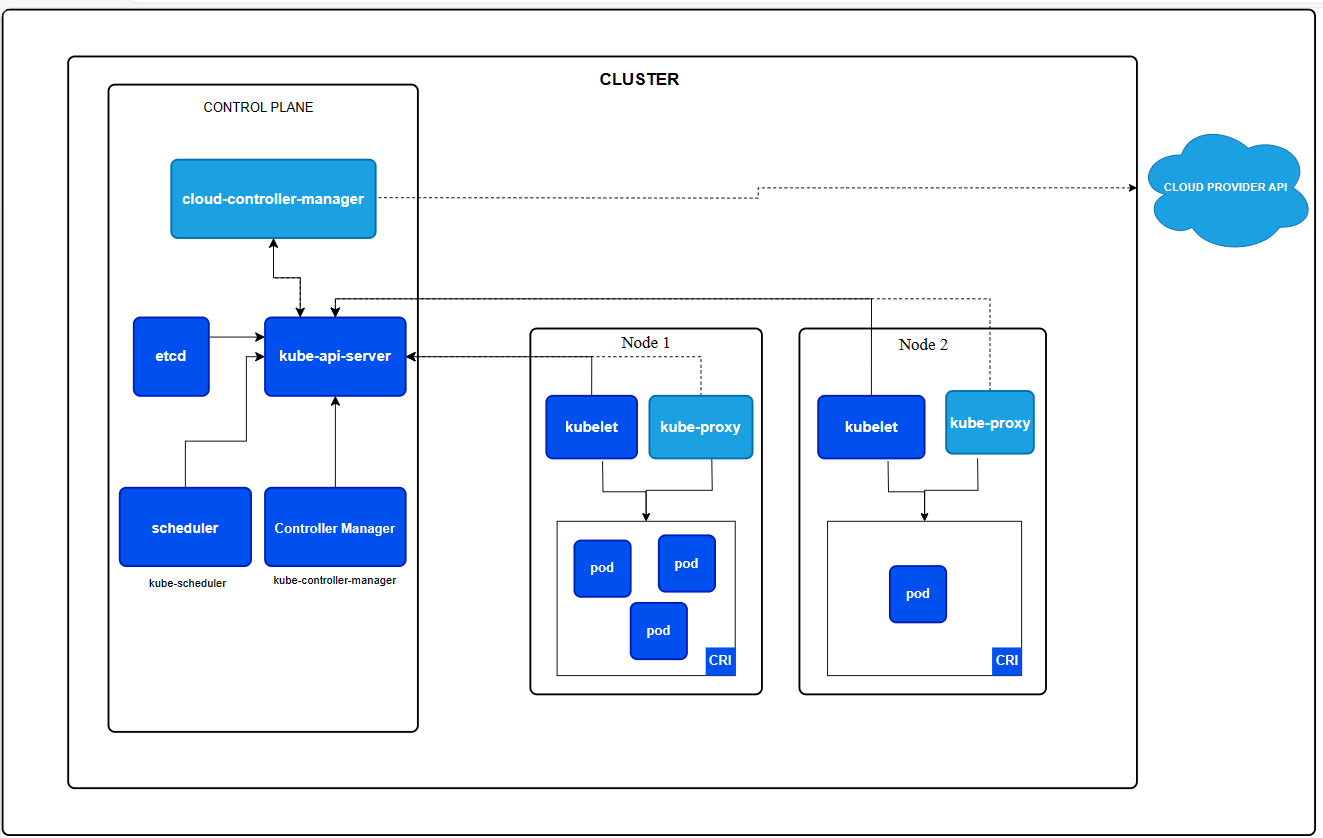
Cluster Architecture
Kubernetes provides you with:
Service discovery and load balancing Kubernetes can expose a container using the DNS name or using their own IP address. If traffic to a container is high, Kubernetes is able to load balance and distribute the network traffic so that the deployment is stable.
Storage orchestration Kubernetes allows you to automatically mount a storage system of your choice, such as local storages, public cloud providers, and more.
Automated rollouts and rollbacks You can describe the desired state for your deployed containers using Kubernetes, and it can change the actual state to the desired state at a controlled rate. For example, you can automate Kubernetes to create new containers for your deployment, remove existing containers and adopt all their resources to the new container.
Automatic bin packing You provide Kubernetes with a cluster of nodes that it can use to run containerized tasks. You tell Kubernetes how much CPU and memory (RAM) each container needs. Kubernetes can fit containers onto your nodes to make the best use of your resources.
Self-healing Kubernetes restarts containers that fail, replaces containers, kills containers that don't respond to your user-defined health check, and doesn't advertise them to clients until they are ready to serve.
Secret and configuration management Kubernetes lets you store and manage sensitive information, such as passwords, OAuth tokens, and SSH keys. You can deploy and update secrets and application configuration without rebuilding your container images, and without exposing secrets in your stack configuration.
Batch execution In addition to services, Kubernetes can manage your batch and CI workloads, replacing containers that fail, if desired.
Horizontal scaling Scale your application up and down with a simple command, with a UI, or automatically based on CPU usage.
IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack Allocation of IPv4 and IPv6 addresses to Pods and Services
Designed for extensibility Add features to your Kubernetes cluster without changing upstream source code
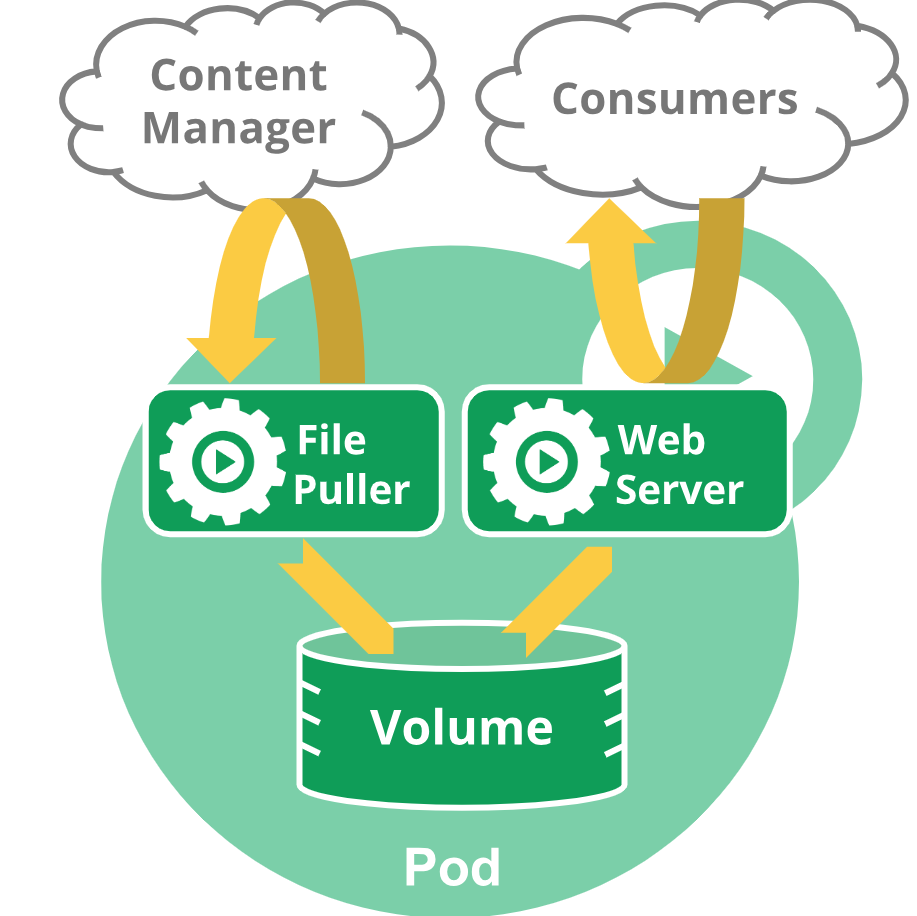
Pods Pods are the smallest deployable units of computing that you can create and manage in Kubernetes.
A Pod (as in a pod of whales or pea pod) is a group of one or more containers, with shared storage and network resources, and a specification for how to run the containers. A Pod's contents are always co-located and co-scheduled, and run in a shared context. A Pod models an application-specific "logical host": it contains one or more application containers which are relatively tightly coupled. In non-cloud contexts, applications executed on the same physical or virtual machine are analogous to cloud applications executed on the same logical host.
What is a Pod? Note: You need to install a container runtime into each node in the cluster so that Pods can run there. The shared context of a Pod is a set of Linux namespaces, cgroups, and potentially other facets of isolation - the same things that isolate a container. Within a Pod's context, the individual applications may have further sub-isolations applied.
A Pod is similar to a set of containers with shared namespaces and shared filesystem volumes
How Pods manage multiple containers